Intro
Computational Geometry is a study of algorithms that pertain to geometry. In relation to game AI, it can involve converting the game world into a data structure that can work for path planning. The process of discretization addresses things like
- Point containment
- line intersections
- triangulation- Breaking down a complicated polygon into more manageable shapes
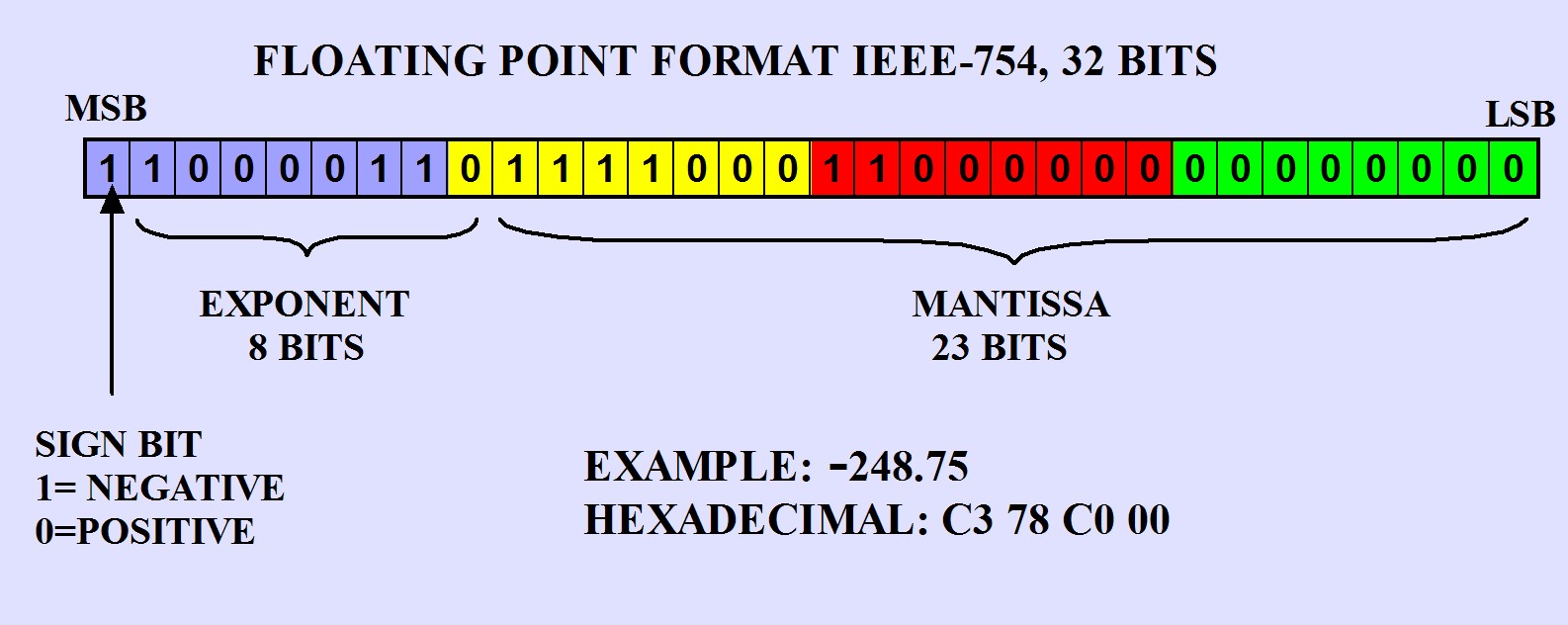
Floating-point vectors
- Floats are represented with bits (typically 32 bits)
- sign bit
- exponent bits
- fraction bits
- Rounding error- hard to have exact representation of a decimal number as a float
Float variation
Floating point with Epsilon
- Epsilon- An area around the target value accepted as “close enough”
Edge cases and point of failure
Integer solution
- Multiply each float by a number (e.g. 1000) and cast to an integer
- This way keeps the fractional part of the float
- Can convert back to floats
When to convert?
- Overhead of converting to integers
- Do the conversion outside of the game
- Bake computational geometry data structures during the build process
- Baking process- after compiling the game, run some tools that prepare the data before deploying the game to a playable process
- In Unity, can bake computationally expensive things in order to cache/preserve the data until the game is run
- NavMesh
- precomputed lighting effects
Integer representation problem
- Overflow
- many languages don’t throw exceptions on an overflow
- Can reorder equation terms to avoid overflow